Chinese Chang’e-4 makes historic landing on moon’s far side
Beijing: No wind blows and no rain falls there. Only crashing meteorites occasionally disrupt the stillness. The desolate landscape on the far side of the moon – never visible from Earth – has waited billions of years to see the first-ever soft landing of a visitor from Earth.
After orbiting the moon for more than 20 days, the Chang’e-4 probe, launched from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in southwest China on December 8, 2018, has seen countless craters, mountains and valleys on the moon.
Finally, its destination on the far side, the South Pole-Aitken (SPA) Basin, the largest, deepest and oldest crater in the solar system, was illuminated by the rising sun.
The developers of Chang’e-4 decided it was the time to come down on this barren world.
At 10:15 a.m., a variable thrust engine was ignited with the assistance of the relay satellite Queqiao (Magpie Bridge), operating in the halo orbit around the second Lagrangian (L2) point of the Earth-moon system, about 65,000 km from the moon, where it can see both Earth and the moon’s far side.
Chang’e-4’s relative velocity to the moon was lowered from 1.7 km per second to close to zero, and the probe was adjusted to face the moon and descend vertically towards the Von Karman Crater in the SPA Basin.
When it descended to an altitude of about 2 km, its cameras captured the shadows of the hills and valleys on the lunar surface. Its computer identified and assessed large obstacles such as rocks and craters, so the probe could avoid them.
At 100 meters up, the probe hovered to identify smaller obstacles and measured the slopes on the surface. Its computer calculated again and selected the safest site.
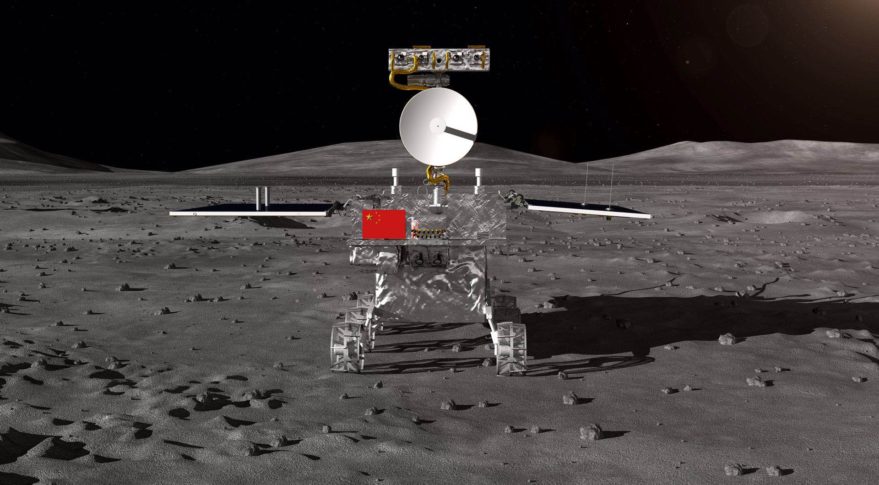
At 2 meters above the surface, the engine stopped, and then the golden lander with a silver rover on top touched down on the desolate gray surface with four legs, throwing up some dust.
The probe performed the entire landing process, lasting about 12 minutes with no intervention from ground control, and the relay satellite transmitted the first close-up photos of the moon’s far side back to a control center in Beijing.
The China National Space Administration later announced that the probe landed at the preselected landing area at 177.6 degrees east longitude and 45.5 degrees south latitude on the far side of the moon.
“It’s an important milestone for China’s space exploration,” said Wu Weiren, chief designer of China’s lunar exploration program.
“It is a perfect display of human intelligence,” said Jia Yang, deputy chief designer of the Chang’e-4 probe, from the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST).
Named after Chinese moon goddess “Chang’e,” China’s lunar exploration program, which began in 2004, includes orbiting and landing on the moon, and bringing samples back to Earth.
After Chang’e-3 completed China’s first soft landing on the moon in 2013, Chinese space experts aimed high, hoping Chang’e-4 could carry out unprecedented and more challenging tasks.
“Landing on the far side of the moon is more risky than landing on the near side. The rugged terrain on the far side has raised many problems,” said Sun Zezhou, chief designer of Chang’e-4 probe, from CAST.
“But solving those problems might help lay the foundation for future space exploration. High-precision landing is a necessity for further exploring the moon and asteroids. We hope to be able to reach the whole moon and even the whole solar system,” Sun said.
“The far side of the moon has unique features never before explored on site,” said Zou Yongliao, director of the lunar and deep space exploration division of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). “The exploration of this virgin land by Chang’e-4 might bring breakthroughs.”
The moon is tidally locked to earth, rotating at the same rate that it orbits Earth, so one side of the moon is seen from Earth, leaving the far side a mystery, until now.
About 60 years ago, the Soviet Union’s Luna 3 probe sent back the first images of the moon’s far side. And about 50 years ago, three astronauts on the United States Apollo 8 mission became the first people to see it with their own eyes.
Lunar orbiters have shown the moon’s two sides are very different: the near side is relatively flat, while the far side is thickly dotted with impact craters of different sizes.
Scientists believe that the lunar crust on the far side is much thicker than the near side. However, the reason is still a mystery. Only on site exploration might reveal the secrets.
The moon and Earth shared a similar “childhood.” But traces of the remote past on Earth have been erased by geological activities. “The moon might provide some insights to the early history of Earth,” said Lin Yangting, a researcher at the Institute of Geology and Geophysics.
Exploring the Von Karman Crater in the SPA Basin is meaningful in another sense. The crater was named after a Hungarian-American mathematician, aerospace engineer and physicist in the 20th century, who was also the teacher of Qian Xuesen and Guo Yonghuai, the founders of China’s space industry.
Nearly 50 years have passed since people first stood on the moon. Can we return? How will radiation on the moon affect astronauts? How much water is there?
Scientists from China, Germany and Sweden hope to find the answers through Chang’e-4, and make preparations for people to return to the moon.
Professor Robert Wimmer-Schweingruber, of the Institute of Experimental and Applied Physics of Kiel University in Germany, said that preparing for future human exploration of the moon was an excellent idea.
“If astronauts come back to Earth, the radiation on the moon is the only danger that remains in their body. So we need to understand that,” he said.
Johan Koehler, head of Solar System Science and Space Situational Awareness, Swedish National Space Agency, said exploration of the far side of the moon was a great achievement by China. “We are very happy to be a part of it.”
“There is a theory that water on the surface of the moon is formed by the interaction of solar wind with the surface regolith. So this is something that Swedish scientists together with Chinese scientists want to answer,” said Koehler.
The Chang’e-4 mission, including the probe, the relay satellite Queqiao and a micro satellite orbiting the moon, is equipped with four payloads developed through international cooperation, providing more opportunities to the world’s scientists and combining human expertise in space exploration.
“I think one of the beauties of space science is that we do cooperate internationally. Space science to me is something important, also as a message of peace worldwide,” Wimmer-Schweingruber said.
For astronomers, the far side of the moon is a place of ideal tranquility, as the body of the moon shields against radio interference from Earth. From there, they can study the origins and evolution of stars and galaxies, peering into the dawn of the universe.
Chang’e-4 carries low-frequency radio astronomical instruments developed by Chinese and Dutch scientists. “Conducting such observation on the moon’s far side is a long cherished goal of astronomers, and could fill gaps in astronomical observation,”said Zou.
The probe also took six live species – cotton, rapeseed, potato, arabidopsis, fruit fly and yeast – to the lifeless environment to form a mini biosphere, which is expected to produce the first flower on the moon.
Chinese space engineers also plan to get data by constantly measuring temperatures on the surface of the moon.
“Exploring the far side of the moon is one contribution China is making to the world. Although we still don’t know what we might find, this exploration might influence several generations,” said Shen Zhenrong, a designer of the lunar rover.
Wu Weiren said: “Exploring the unknown is human nature. The moon is a mysterious world to us. We have a responsibility to explore and to understand it. Exploration of the moon will also deepen our understanding of Earth and ourselves.”





